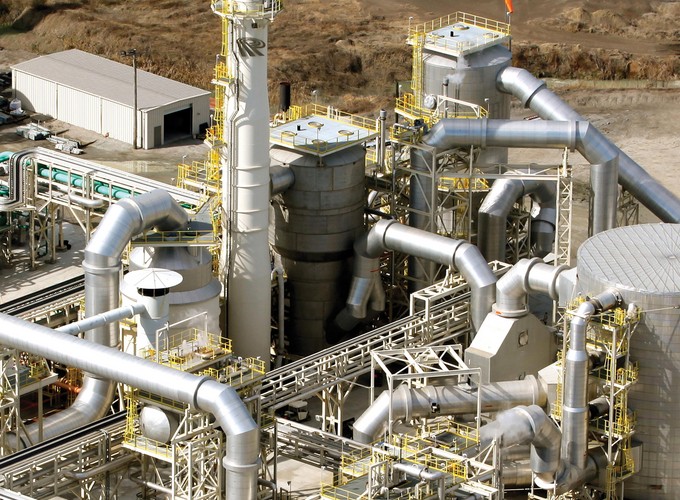
Over the past century, the number of sulfuric acid plants operating globally has expanded exponentially. Throughout the 20th century, rapid industrial growth in combination with increasing demand for superphosphate fertilizers led to high demand for the “king of chemicals,” sulfuric acid….
Acid Absorption Tower Problems through Process Parameters
A poorly performing absorbing tower can manifest in poor stack appearance, bad stick test results, bad acid emission testing results, as well as acid sulfate splotches on nearby structural steel members and grade. Absorbing towers are equipped with mist eliminator elements…
Sulphuric Acid in the Age of Technology
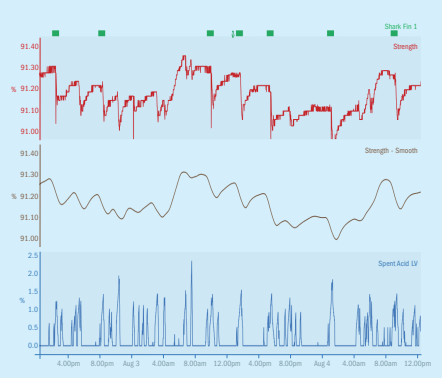
In today’s dynamic business landscape, digitalization has become a powerful tool for companies seeking to enhance operations. By leveraging real-time plant data, organizations can create more meaningful interactions between operations teams, technical experts within the industry and the power of machine…
IsoTherming Hydroprocessing – A Hydroprocessing Revamp Solution for Carbon Footprint Reduction
In the age of energy transition, the value of exploring more efficient and economicalprocesses to produce fuels reducing utilities is becoming much higher. The IsoTherming® hydroprocessing technology offers a cost-effective solution to revamp existingunits to consistently reduce utility consumption and increase…
New Impaction Technology for Acid Plant Towers
MECS, Inc. (MECS) has developed a new impaction-based mist eliminator called Brink® Prime Impact™, which offers equivalent or improved efficiency at higher throughput and the same pressure drop as traditional impaction beds, resulting in the ability to debottleneck existing interpass absorption…
Hydrogen Safety in Sulphuric Acid Plants
Safety in sulphuric acid plants is a well-known and widely discussed topic. Industry turnover is a reality, and keeping new employees informed of hydrogen safety procedures is key to keeping plants fully operational and
incident free. Walter Weiss of Elessent Clean Technologies discusses the steps facilities need to take to prevent hydrogen incidents.
Equipped for a Cleaner Future
Anew age of fuel production is here with the introduction of policy changes pushing refineries to reduce emissions and ultimately achieve net zero goals. These policies include compliance and voluntary carbon markets that play an important role in driving refineries to make investments towards a more sustainable future. The carbon markets utilise tax credits that are available to refineries that can produce fuels in a more efficient and sustainable manner. One avenue to receiving
carbon market tax credits is to improve energy efficiency by reducing emissions generated through utilities. This can be done by measuring and optimising utility consumption, such as fuel gas, steam, cooling water and electricity, and then converting to the equivalent amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions that were reduced. In addition to this, traditional fossil fuel feedstocks can be replaced by feedstocks made from renewable resources that are harder to process, such as
vegetable oils, bioethanol, and animal fats, but that are also eligible as carbon market tax credits.
Fuels of the Future
The global fuels market will see a dramatic shift over the next 10 years. Despite its steep reduction in demand in 2020 due to the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, global liquid fuel consumption is expected to surpass pre-pandemic levels sometime in 2022. Stricter fuel specifications, a changing vehicle fleet, the growing role of alternative fuels and the potential for a tightening crude market will determine developments of the fuel market through to 2030 and beyond. Europe has been leading the way towards cleaner, lower-emission fuels. The proposed Euro 7 standards are set to feature even stricter rules on emission levels for all gasoline and diesel cars, vans, trucks and buses. Other industrialised regions of the world are likely to follow. The pandemic has also accelerated the trend to decarbonise, reduce emissions and incorporate renewable fuels.
Reducing Acid Consumption: Maximizing Sulfuric Acid Alkylation Unit Profitability
Alkylation is a process used to produce highly branched isoparaffins from the reaction of lighter olefins and isobutane in the presence of sulfuric acid as a catalyst. This highly branched isoparaffins is called alkylate – a blending component that constitutes approximately 10% – 15% of the gasoline pool in the U.S. Besides the ability to increase octane and lower Reid vapor pressure (RVP) in the gasoline pool, alkylate also reduce vehicles exhaust emissions with zero olefins, zero aromatics and low sulfur.
MECS® Advanced Catalysts Help Manage and Reduce Sulphuric Acid Plant Emissions
Catalyst is at the heart of all sulphuric acid plants and plays a critical role
in plant performance. This article provides an overview of the specific design
features of two new types of MECS® sulphuric acid catalyst developed by DuPont Clean Technologies (DuPont), XLP-310 and SuperGEAR™, and explains how these more advanced catalyst types can be applied to reduce emissions or increase the capacity of a sulphuric acid plant.